Extranodal lymphoma (Liver, spleen, adrenal glands and bone marrow): 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging
A 68-year-old male was transferred to our hospital because of an impairment of his general condition, weight loss and fever in the last 20 days. Dyspnea and splenomegaly were observed. The patient had anemia (3,00^12/L; reference 3,9 – 5,5) and thrombocytopenia (42^9/L; reference 130 – 400).
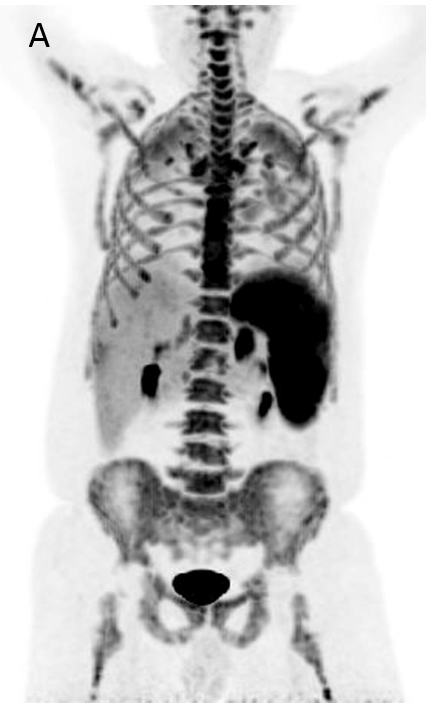
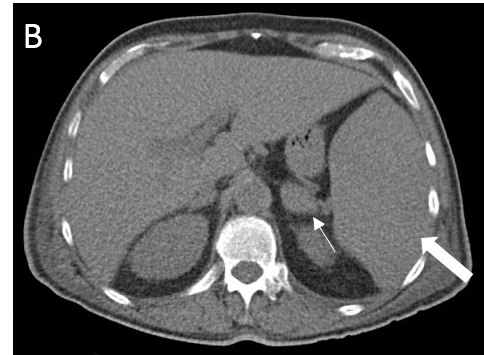
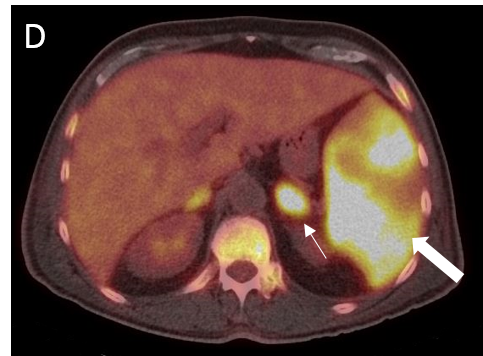
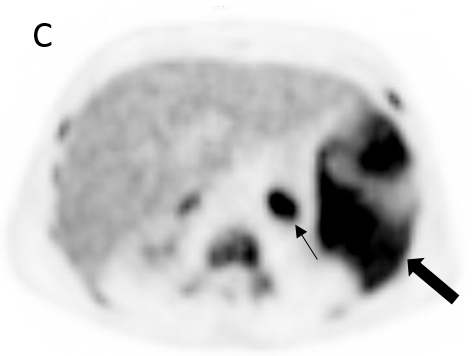
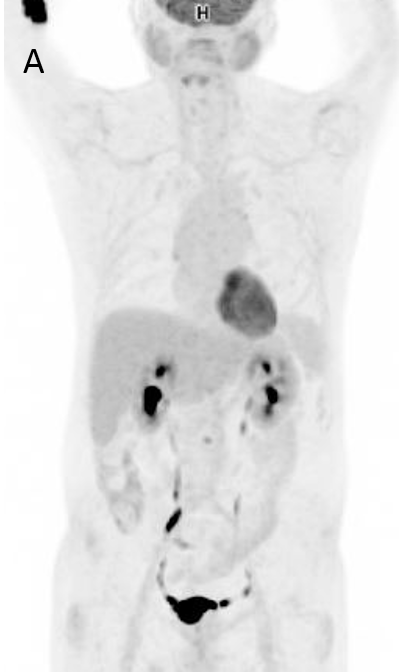
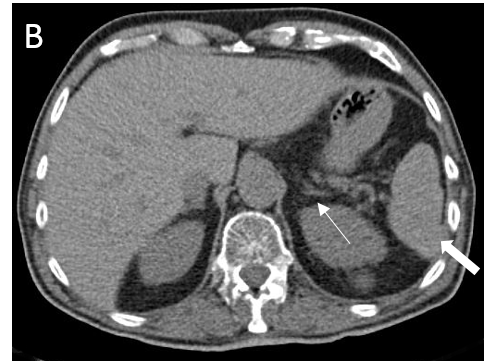
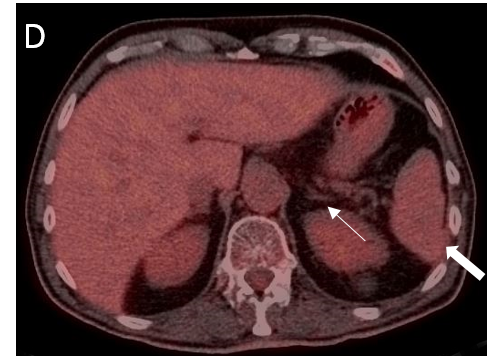
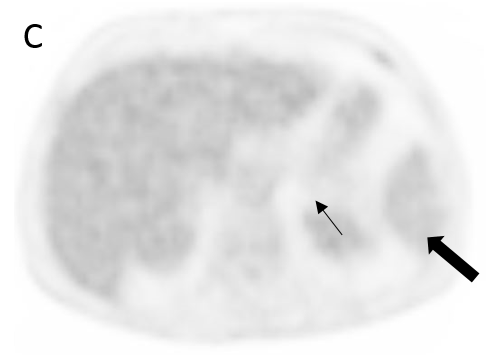
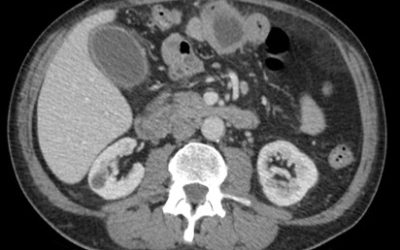
FIGURE 1.
A 18F- FDG PET/CT scan was performed, as a hematology malignancy was suspected. The maximum intensity projection in image (A) demonstrated an abnormally increased FDG uptake, located in bone marrow, spleen and left adrenal. Moderate FDG uptake in the right adrenal. The axial images (B, non contrast CT; C, PET; D, PET/CT fusion) showed an splenomegaly of 17 cm with heterogeneous FDG uptake with SUVmax 10,7 (small arrow) and hypertrophy of left adrenal with diffuse uptake 3,6×2 cm and SUVmax being 12 (large arrow). Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma was diagnosed after a bone marrow biopsy in the sternum. Extranodal lymphoma (Liver, spleen, adrenal glands and bone marrow) was determinded since no lymph nodes were pathological.
FIGURE 2.
After six-cycles of chemotherapy with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisolone (R-CHOP), the patient showed a complete response, being classified as Deauville Score 2.
The maximum intensity projection image (A) demonstrated physiological FDG uptake with normalization of the uptake in the bone marrow. The axial images (B, non contrast CT; C, PET; D, PET/CT fusion) showed a reduced FDG uptake and size in the spleen and left adrenal.
More Cases:
Case No. 22
Primary intestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
Case No. 21
Primary carcinoid tumor of the lung
Case No. 20
Takayasu arteritis: 18F-FDG-PET/CT